In an increasingly cashless world, businesses of all sizes—from neighborhood cafés to global e-commerce platforms—rely on merchant services to accept payments securely and efficiently. “Merchant services” is an umbrella term encompassing the tools, accounts, and processes that enable a business to process debit, credit, mobile, and online transactions.
Far beyond simple card readers, modern merchant service solutions integrate payment gateways, point-of-sale (POS) software, fraud prevention, reporting dashboards, and value-added features such as loyalty programs. Understanding how these services work, why they’re essential, and how to choose the right provider is vital for any organization seeking to streamline operations, enhance customer experience, and boost revenue.
What Are Merchant Services?

At its core, merchant services refers to the suite of products and solutions that allow a business to accept electronic payments. Key components include:
- Merchant Account: Merchant account provider offers specialized bank account that temporarily holds funds from card transactions before they are deposited into the business’s primary account.
- Payment Gateway: The secure, online interface that encrypts and transmits cardholder data between a website or terminal and the payment processor.
- Payment Processor: The financial institution or third-party company that routes transaction data, obtains authorization from the cardholder’s bank, and facilitates fund settlement.
- Point-of-Sale (POS) System: Hardware and software used in physical locations to accept payments, manage inventory, and print receipts.
- Security & Compliance Tools: EMV chip readers, end-to-end encryption (E2EE), and tokenization services designed to protect sensitive payment data and ensure compliance with the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS).
Together, these components form an end-to-end payment ecosystem that handles every step—from a customer tapping their contactless card or entering details online, to funds appearing in the merchant’s bank account.
Why Businesses Need Merchant Services
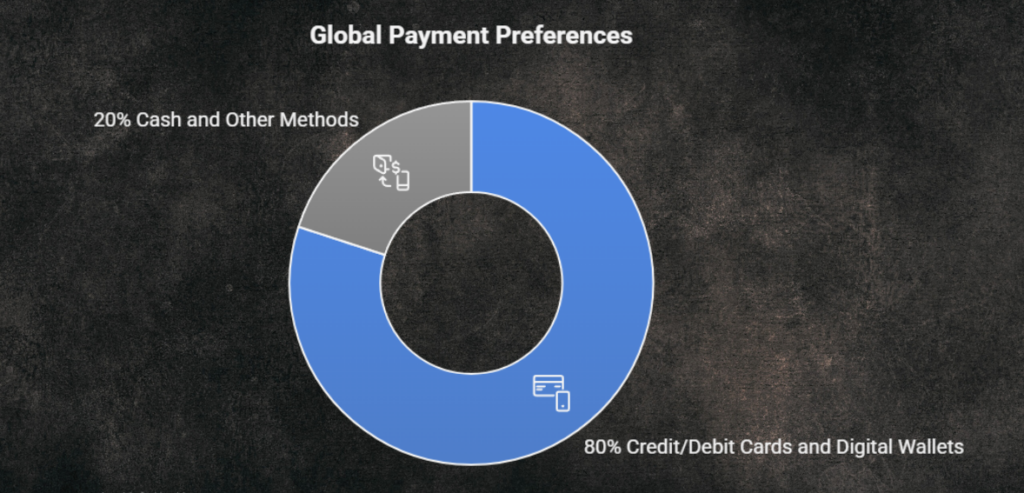
- Capture More Sales:
Over 80% of consumers globally now prefer to pay using credit/debit cards or digital wallets, making electronic payment acceptance essential for capturing the majority of potential sales. Relying solely on cash can alienate customers and significantly limit your business’s reach.
In addition, high-value transactions—such as those involving electronics, home appliances, and travel bookings—are rarely paid for with cash. Accepting card payments opens the door to these larger purchases and helps increase average transaction values.
- Enhance Customer Experience:
Speed and convenience are key to customer satisfaction, and merchant services deliver both by enabling fast, contactless, and mobile payments that reduce checkout times and waiting lines. This streamlined process leads to quicker service and happier customers.
Furthermore, integrated POS systems and e-commerce platforms allow businesses to offer a seamless omnichannel experience, where customers can switch between online and in-store shopping without disruption, thereby improving brand loyalty and trust.
- Improve Cash Flow & Reporting:
Merchant services speed up the payment cycle, with most card transactions settling in one to two business days—much faster than the manual processing times of checks or cash deposits. This quicker access to funds improves cash flow, which is vital for covering operational expenses.
Additionally, many merchant service platforms offer real-time analytics that help businesses track sales performance, monitor peak hours, and manage inventory, giving owners the insights needed to make data-driven decisions that optimize performance.
- Strengthen Security & Compliance:
Security is a major concern in electronic transactions, and merchant services help mitigate risks through built-in fraud detection tools, including real-time risk scoring and transaction monitoring.
These features help spot suspicious activity before it results in chargebacks or financial losses. Providers also assist businesses in maintaining PCI DSS compliance by offering the necessary tools and support to secure customer data, thereby reducing the risk of breaches and avoiding regulatory penalties.
- Differentiate Your Business:
Merchant services often include value-added features like loyalty programs, branded gift cards, and promotional tools that encourage repeat business and deepen customer engagement. These enhancements can significantly boost customer retention and overall sales.
Additionally, offering modern, secure, and convenient payment options helps businesses project a more professional image. Customers are more likely to trust and return to businesses that keep up with current payment technologies and provide flexibility at checkout.
How Merchant Services Work: A Transaction Lifecycle
The entire lifecycle takes place in four different breaks:
Authorization
- The customer presents their card (in-person), taps/swipes it into the POS terminal, or enters card details on a website.
- The payment gateway encrypts this data and sends it to the payment processor.
- The processor routes the request to the card network (Visa, Mastercard, etc.), which asks the issuing bank for authorization.
- The bank approves or declines based on card status, available funds, and risk factors.
- The gateway returns an approval code (or decline message) to the merchant and customer.
Batching
- Approved transactions are stored in a “batch” by the merchant’s terminal or software, typically closed at the end of each business day.
- Batching optimizes processing costs by submitting multiple transactions in a single file.
Clearing & Settlement
- The processor forwards the batch file to the respective card networks, which then coordinate fund transfers from issuing banks to the merchant’s acquiring bank.
- Funds are deposited into the merchant account, minus processing fees, and then swept into the business’s primary bank account.
Funding
- Depending on the provider and account settings, merchants receive payouts daily or multiple times per week.
- Real-time and next-day funding options are increasingly common for cash-flow-critical operations.
Types of Merchant Service Providers
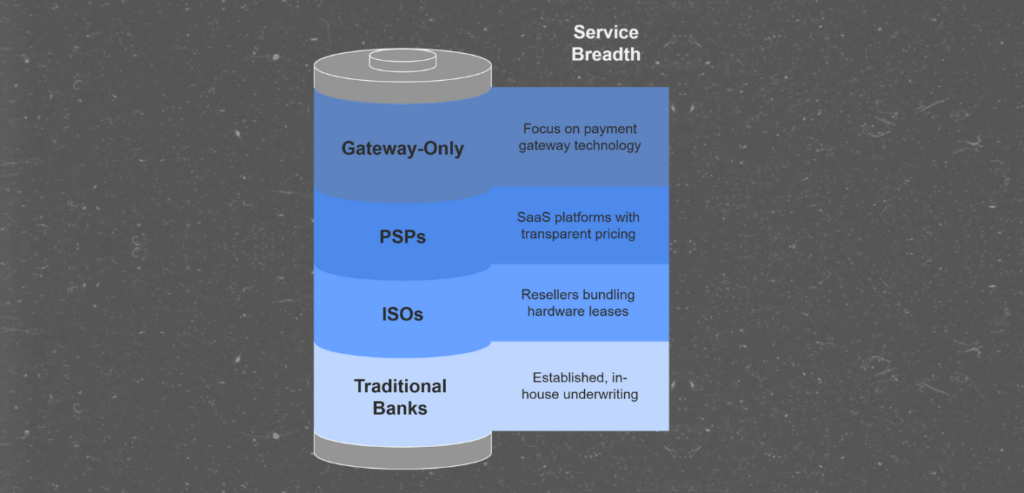
| Provider Type | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Traditional Banks & Acquirers | Full banking services, established reputations, potentially higher fees, in-house underwriting. |
| Independent Sales Organizations (ISOs) | Third-party resellers; often bundle processing with hardware leases; may offer flexible plans. |
| Payment Service Providers (PSPs) | Integrated SaaS platforms (e.g., Stripe, Square); no separate merchant account required; developer-friendly APIs; transparent pricing. |
| Gateway-Only Providers | Specialize solely in payment gateway technology; require merchants to contract separately for accounts and processing. |
Core Merchant Service Features
- Multi-Channel Acceptance: In-store terminals, mobile card readers, online checkout pages, and invoice billing.
- Advanced Security: EMV chip & PIN, point-to-point encryption (P2PE), tokenization, and 3D Secure for e-commerce.
- Seamless Integration: Plugins for popular e-commerce platforms (Shopify, WooCommerce), accounting software (QuickBooks, Xero), and ERP systems.
- Customizable Hardware: Countertop terminals, wireless/mobile readers, unattended kiosks, and smart terminals that double as mini-computers.
- Value-Added Services: Gift and loyalty programs, automated chargeback management, installment payments (Buy Now, Pay Later), and multi-currency support.
- Reporting & Analytics: Sales dashboards, end-of-day summaries, customer purchasing patterns, and inventory alerts.
Pricing Models & Fees
Selecting a pricing plan that aligns with your transaction volume and mix is crucial. Common models include:
- Flat-Rate Pricing: A single percentage (e.g., 2.9% + $0.30) for all card types. Simplicity at the cost of potential overpaying on low-risk, high-volume transactions.
- Interchange-Plus (Cost-Plus) Pricing: Passes through the card network’s interchange fee plus a fixed markup. Transparent and often the most cost-effective for mid- to high-volume merchants.
- Tiered Pricing: Buckets transactions into “qualified,” “mid-qualified,” and “non-qualified” tiers with different rates. Can be confusing and opaque; rate definition varies by provider.
- Subscription / Membership Pricing: Monthly fee for software access, plus minimal per-transaction charges.Predictable costs; may benefit high-volume businesses.
- Additional Charges: Monthly gateway fees, PCI compliance fees, chargeback fees, terminal rental or purchase costs, setup/termination fees.
Tip: Always request a sample statement, scrutinize each fee line, and calculate the “effective rate” based on your average ticket size and monthly processing volume.
Benefits of Merchant Services
| Business Benefit | Impact |
|---|---|
| Revenue Growth | Capture sales from card-preferring customers; enable impulse purchases through convenient checkout. |
| Operational Efficiency | Automated batching, digital receipts, and integrated inventory reduce manual errors and save time. |
| Improved Cash Flow | Faster settlements and flexible funding schedules optimize working capital. |
| Enhanced Customer Loyalty | Branded gift cards, rewards, and personalized promotions encourage repeat business. |
| Data-Driven Insights | Analytics on sales patterns, peak hours, and customer behavior support strategic planning. |
| Fraud Protection & PCI Compliance | Robust security tools and managed compliance reduce liability and protect brand reputation. |
| Global Expansion | Multi-currency and cross-border payment support unlocks international markets. |
How to Choose the Right Merchant Service Provider
- Assess Business Needs: Transaction volume, average ticket size, sales channels (in-store vs. online), and growth projections.
- Compare Pricing Structures: Request detailed fee schedules; calculate estimated monthly costs under realistic sales scenarios.
- Evaluate Feature Sets: Prioritize essential capabilities (e.g., EMV compliance, reporting, multi-channel integration) and identify nice-to-haves (gift cards, financing).
- Test Usability & Support: Demonstrations of POS software, trial accounts for gateway integration, and 24/7 customer service availability.
- Check Compatibility & Integration: Ensure seamless connection with existing e-commerce platforms, accounting systems, and CRM tools.
- Review Security & Compliance Credentials: Confirm PCI DSS certification, data-security practices, and liability shift details (e.g., EMV liability protection).
- Read Customer Reviews & References: Seek feedback on reliability, rate transparency, and support responsiveness from similar merchants.
- Negotiate Terms: Many providers are open to custom pricing, especially for merchants with stable volume or committed multi-year contracts.
Conclusion
Merchant services are far more than just a mechanism to swipe or key in payment cards. They are the backbone of modern commerce, empowering businesses to offer seamless, secure, and versatile payment experiences across physical and digital channels.
By understanding the core components—merchant accounts, gateways, processors, POS systems—and evaluating providers based on pricing, features, security, and support, organizations can optimize their checkout flow, enhance customer satisfaction, and unlock new revenue streams. As payment technologies continue to evolve—with contactless wallets, subscription billing, and AI-driven fraud prevention—staying informed and agile will ensure businesses remain competitive in a cashless, connected economy.
